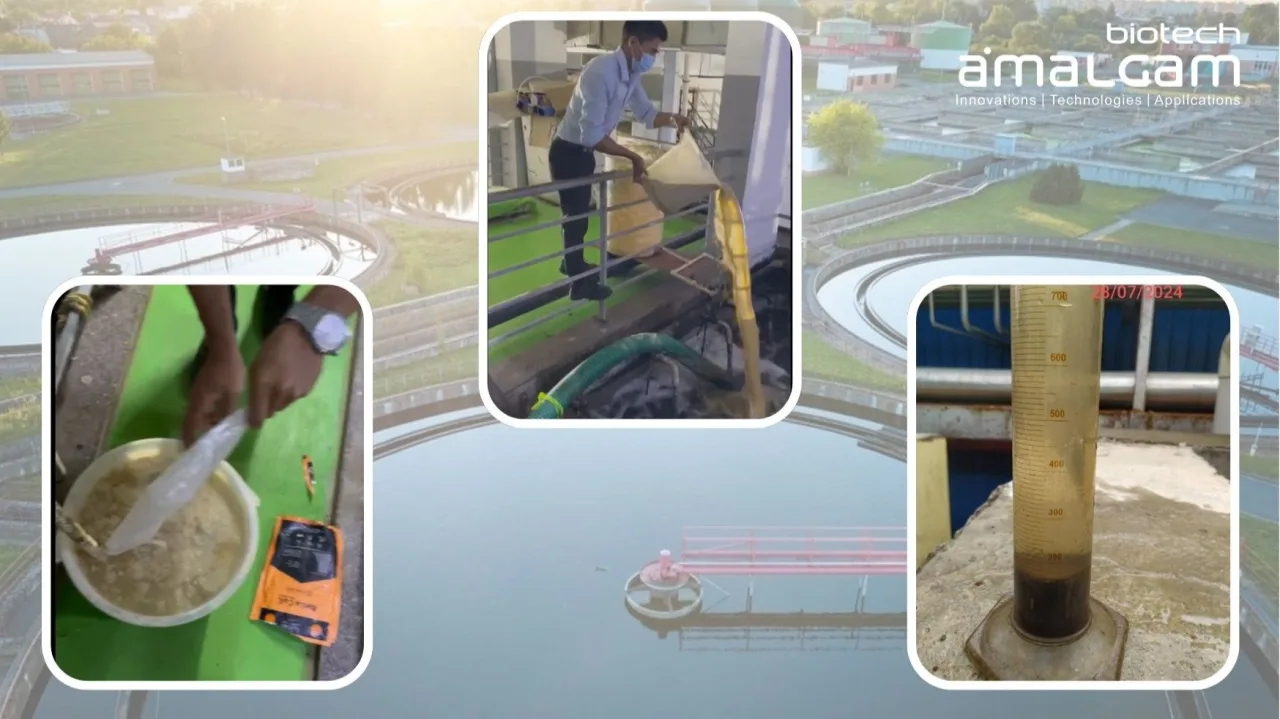
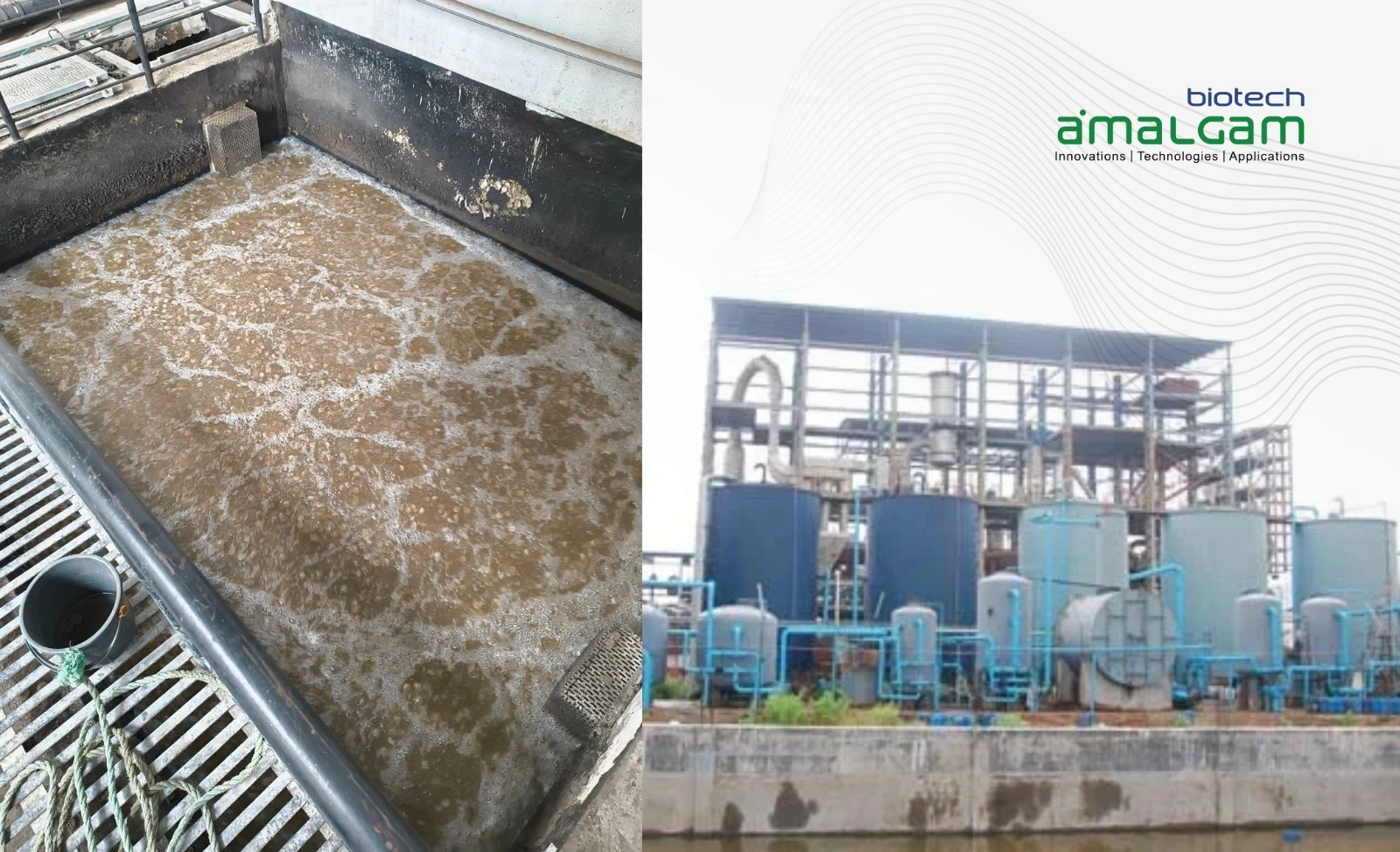
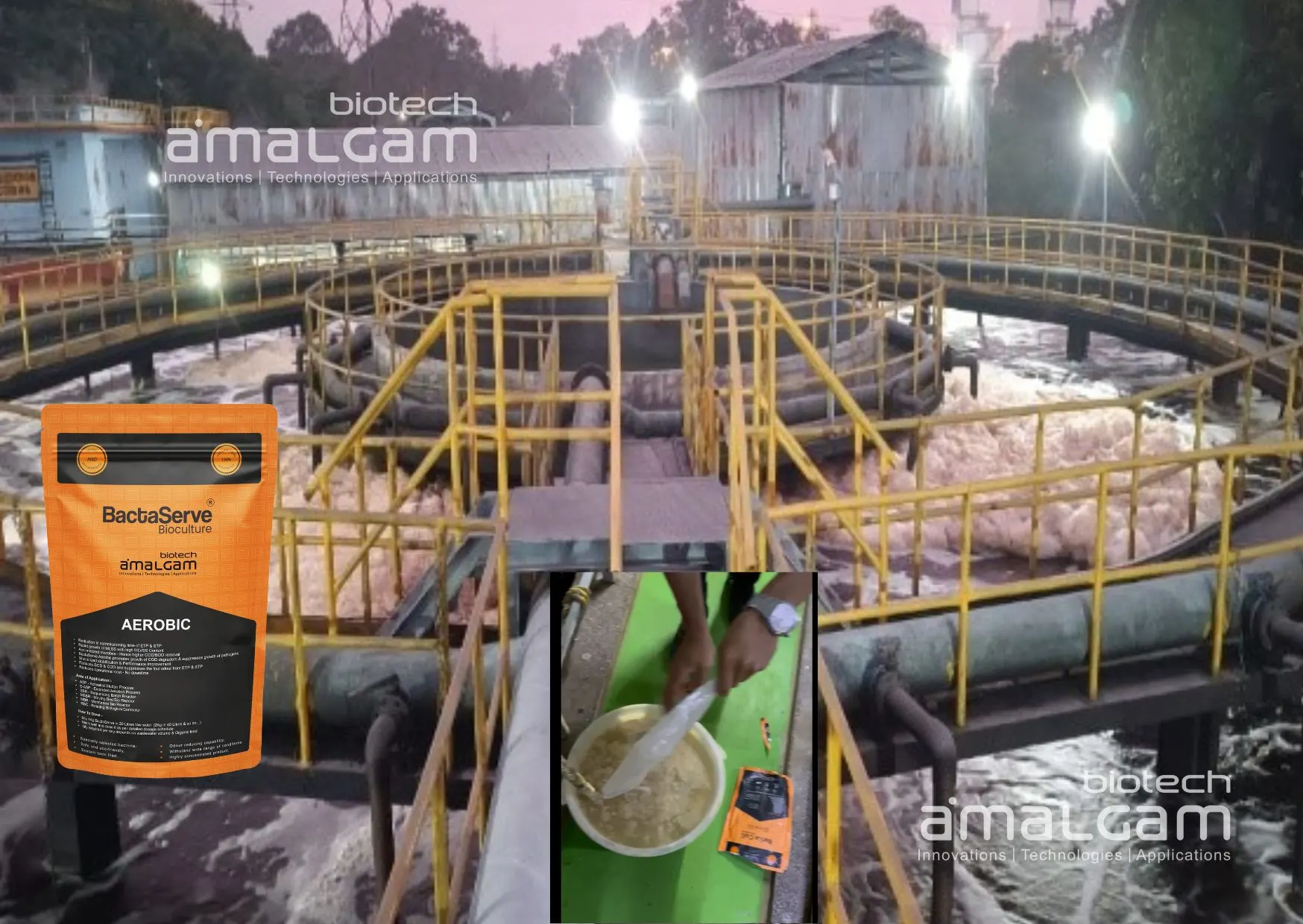
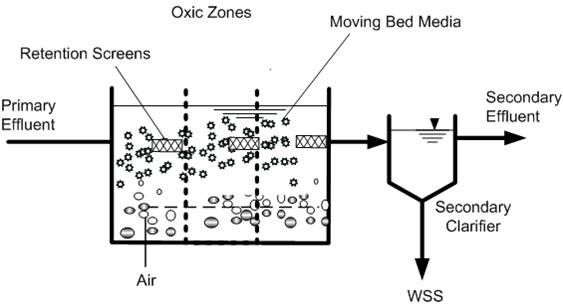
Effluent Treatment Plants (ETPs) play a critical role in protecting our environment. They're essential for treating wastewater generated from various sources, including industries like textiles, pharmaceuticals, food processing, and municipalities. While ETPs involve a complex network of physical and chemical processes, a crucial element often overlooked is the role of bio culture for ETP.
Think of bio culture for ETP as a workforce of microscopic superheroes working tirelessly to break down pollutants and purify wastewater. These cultures consist of a carefully selected blend of microorganisms, specifically bacteria, that thrive in the ETP environment and accelerate the biodegradation of organic waste. This biological process is at the heart of effective wastewater treatment.
Why is Bio Culture Essential for Your ETP?
Neglecting the health and effectiveness of your bio culture for ETP can lead to a cascade of problems, including reduced treatment efficiency, increased operating costs, and even environmental violations. Here's a deeper look at why prioritizing bio culture is crucial:
1. Enhanced Treatment Efficiency:
Accelerated Biodegradation: Bio culture for ETP significantly speeds up the decomposition of organic pollutants, improving the overall efficiency of the treatment process. This ensures that wastewater is treated to the required standards before being discharged. These microorganisms essentially "eat" the organic waste, converting it into harmless byproducts.
Improved BOD and COD Removal: Biological Oxygen Demand (BOD) and Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD) are important markers of wastewater pollution. Effective bio culture for ETP helps reduce these levels, ensuring compliance with environmental regulations. High BOD and COD levels indicate a high concentration of organic pollutants, which can deplete oxygen in receiving water bodies and harm aquatic life.
Reduced Sludge Generation: Efficient biodegradation can lead to reduced sludge generation, minimizing disposal costs and environmental impact. Sludge is the solid residue that settles out during wastewater treatment. Reduced sludge volume means cheaper costs for handling, transportation, and disposal.
2. Cost Savings:
Reduced Chemical Usage: A healthy bio culture for ETP can reduce the need for harsh chemicals, leading to significant cost savings in the long run. Chemicals like coagulants and flocculants are often used in wastewater treatment, but a thriving bio culture can reduce their requirement.
Lower Energy Consumption: Efficient biodegradation reduces the energy required for aeration and other processes, further contributing to cost savings. Aeration is essential for providing oxygen to the microorganisms, but a healthy bio culture can reduce the aeration intensity and duration.
Minimized Maintenance: A well-maintained bio culture for ETP can prevent operational issues and reduce the need for costly repairs and maintenance. By preventing blockages, clogging, and other issues, bio culture contributes to smoother ETP operation.
3. Environmental Compliance:
Meeting Discharge Standards: Effective bio culture for ETP ensures that treated wastewater meets the stringent discharge standards set by environmental regulatory bodies. These standards vary by region and industry, but they all aim to protect water quality and public health.
Protecting Water Resources: By effectively removing pollutants, bio culture for ETP helps protect our precious water resources and maintain the health of aquatic ecosystems. This is crucial for preserving biodiversity and ensuring the sustainability of our water resources.
4. Increased System Stability:
Resistance to Shock Loads: A robust bio culture for ETP can better withstand sudden changes in wastewater composition or flow, preventing system upsets and maintaining consistent treatment efficiency. Industrial wastewater can vary significantly in its composition, and a strong bio culture can adapt to these fluctuations.
Faster Recovery: In case of operational disruptions, a healthy bio culture for ETP can help the system recover faster and resume optimal performance. This resilience is crucial for minimizing downtime and ensuring consistent wastewater treatment.
Choosing the Right Bio Culture for Your ETP
Selecting the appropriate bio culture for ETP is crucial for achieving optimal results.
Factors to consider include:
Wastewater Characteristics: The type and concentration of pollutants in the wastewater will influence the choice of bio culture. For example, industrial wastewater with high levels of specific contaminants, such as heavy metals or toxic chemicals, may require specialized bio cultures that can tolerate or degrade those substances.
ETP Design and Operating Conditions: The specific design and operating parameters of the ETP should be considered when selecting a bio culture. This includes factors like hydraulic retention time (the time wastewater spends in the treatment system), aeration capacity, and sludge handling methods.
It's recommended to consult with experts in wastewater treatment and bio culture for ETP to determine the most suitable option for your specific needs. They can conduct laboratory analysis and pilot studies to identify the most effective bio culture for your ETP, considering factors like the microbial diversity and their ability to degrade specific pollutants.
Maintaining a Healthy Bio Culture
Once you've introduced bio culture for ETP, it's essential to maintain its health and effectiveness. This involves:
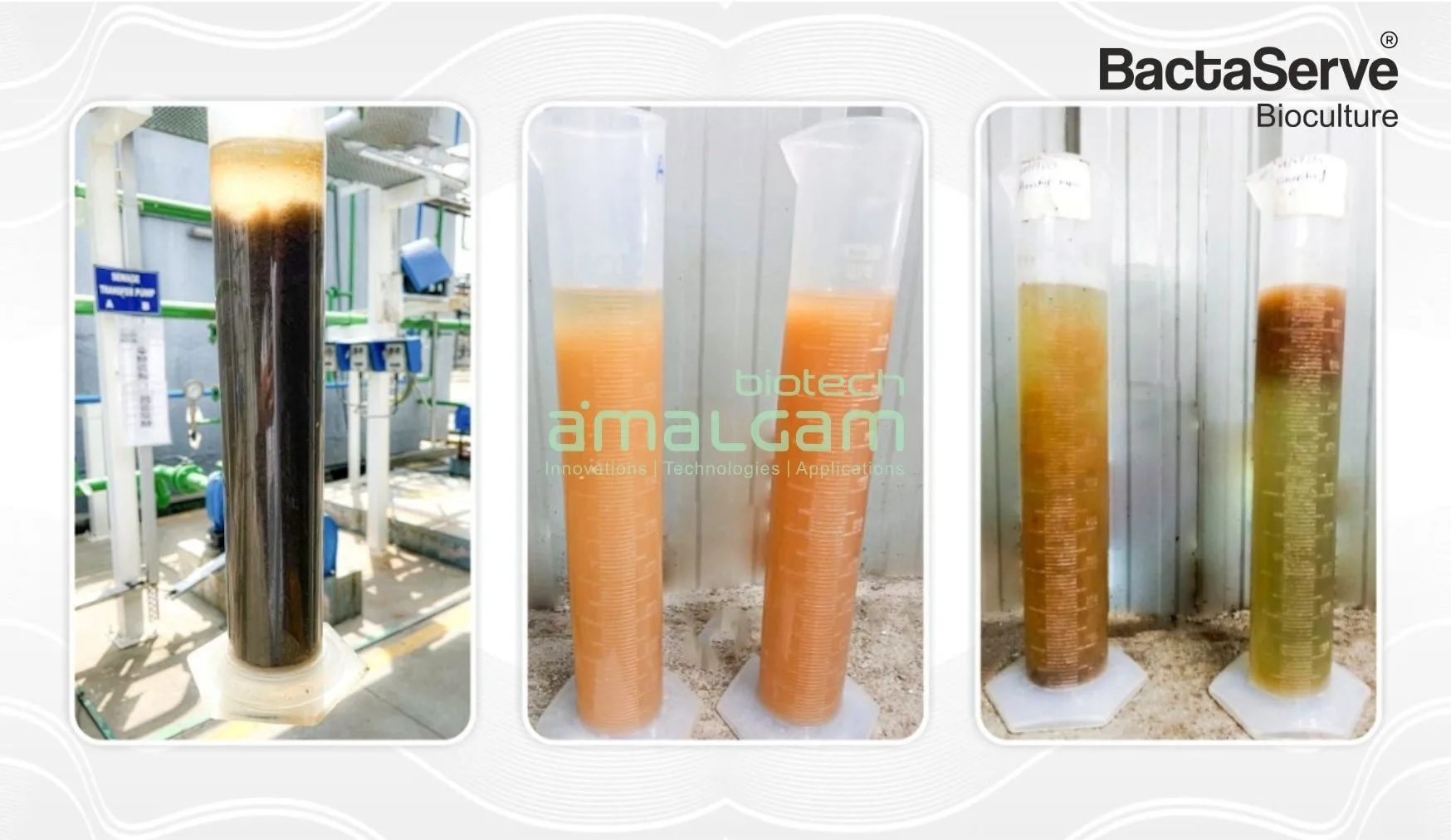
Regular Monitoring: Regularly monitor key parameters like BOD, COD, and MLSS (Mixed Liquor Suspended Solids) to assess the performance of the bio culture. This helps to discover possible concerns early on and enables for timely corrective action. Deviations from normal ranges can indicate problems with the bio culture or the treatment process itself.
Nutrient Supplementation: Ensure adequate nutrient levels are maintained to support the growth and activity of the microorganisms. This may involve adding nitrogen and phosphorus to the wastewater if necessary. These nutrients are essential for microbial metabolism and reproduction.
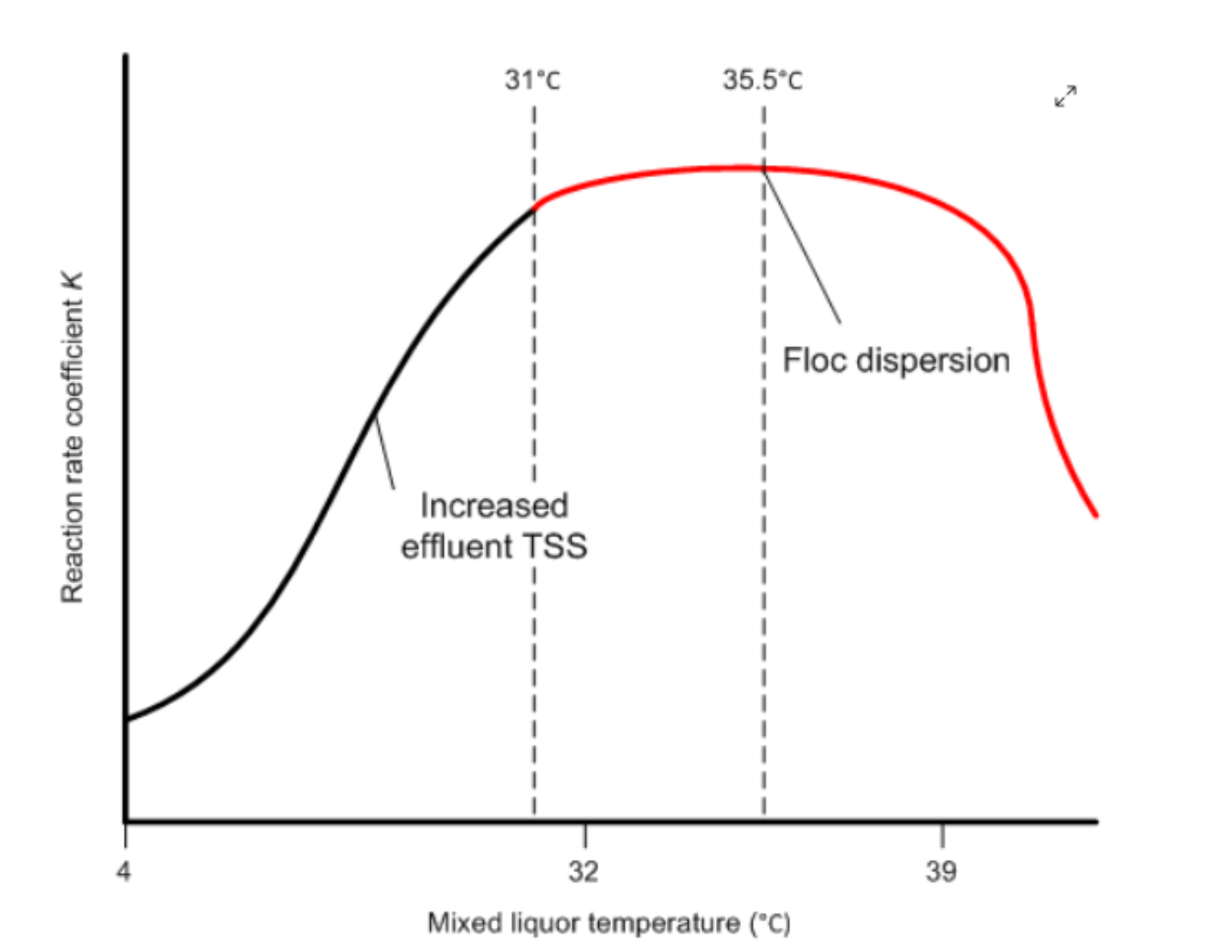
Optimal Operating Conditions: Maintain the appropriate environmental conditions, including temperature, pH, and dissolved oxygen levels, to promote optimal bio culture activity. This may require adjustments to aeration rates, mixing patterns, and other operational parameters. Extremes in temperature or pH can inhibit microbial activity, while insufficient dissolved oxygen can hinder aerobic degradation.
The Future of Bio Culture in ETPs
With increasing emphasis on sustainable and environmentally friendly solutions, the role of bio culture for ETP is becoming even more critical. Ongoing research and development are focused on:
Developing specialized bio cultures: Scientists are working to develop specialized bio cultures that can target specific pollutants, such as pharmaceuticals and personal care products, which are increasingly found in wastewater. These emerging contaminants pose new challenges for wastewater treatment, and specialized bio cultures offer a promising solution.
Improving bioaugmentation techniques: Researchers are exploring new techniques to enhance the introduction and establishment of bio culture for ETP, ensuring faster acclimatization and improved performance. This includes techniques like immobilization of microorganisms on carrier materials and the use of pre-acclimated cultures.
Integrating bio culture with other technologies: Efforts are underway to integrate bio culture with other advanced treatment technologies, such as membrane bioreactors, to further enhance treatment efficiency. Membrane bioreactors combine biological treatment with membrane filtration to achieve higher levels of purification.
By embracing the power of bio culture for ETP, we can ensure efficient wastewater treatment, protect our environment, and contribute to a sustainable future. Don't neglect this vital component of your ETP – invest in the right bio culture and reap the benefits of a healthy and efficient wastewater treatment system.