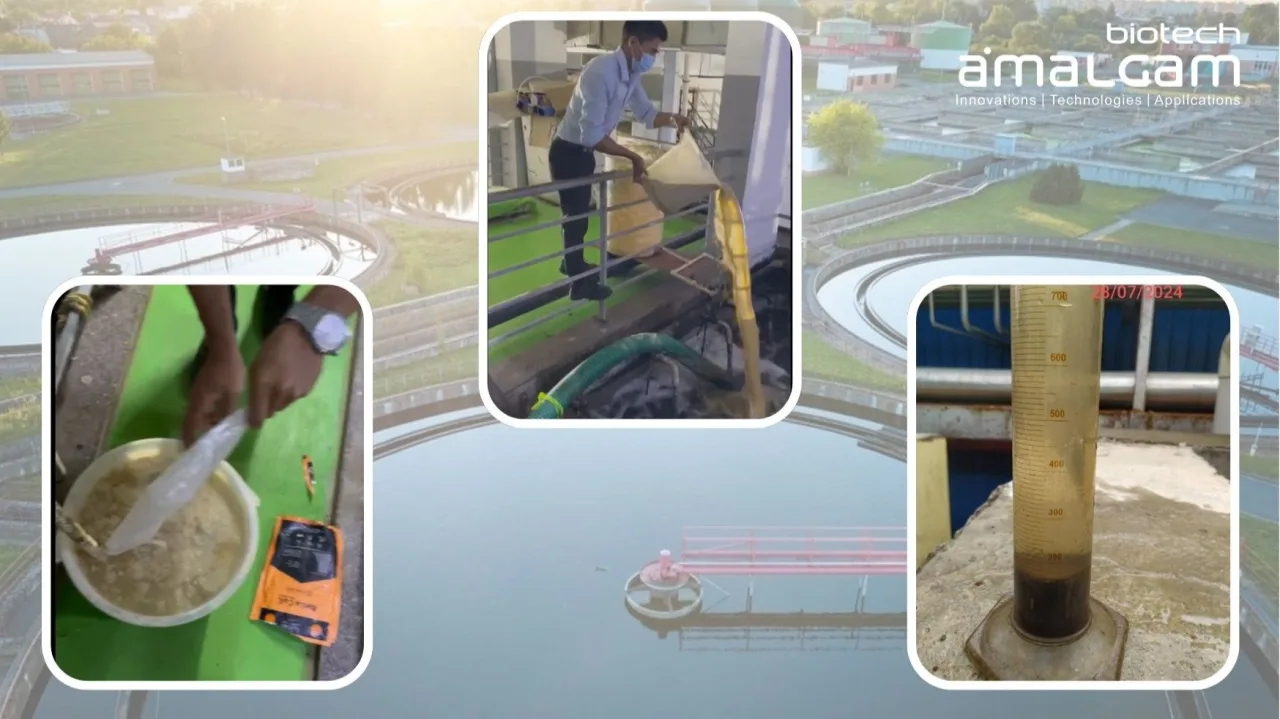
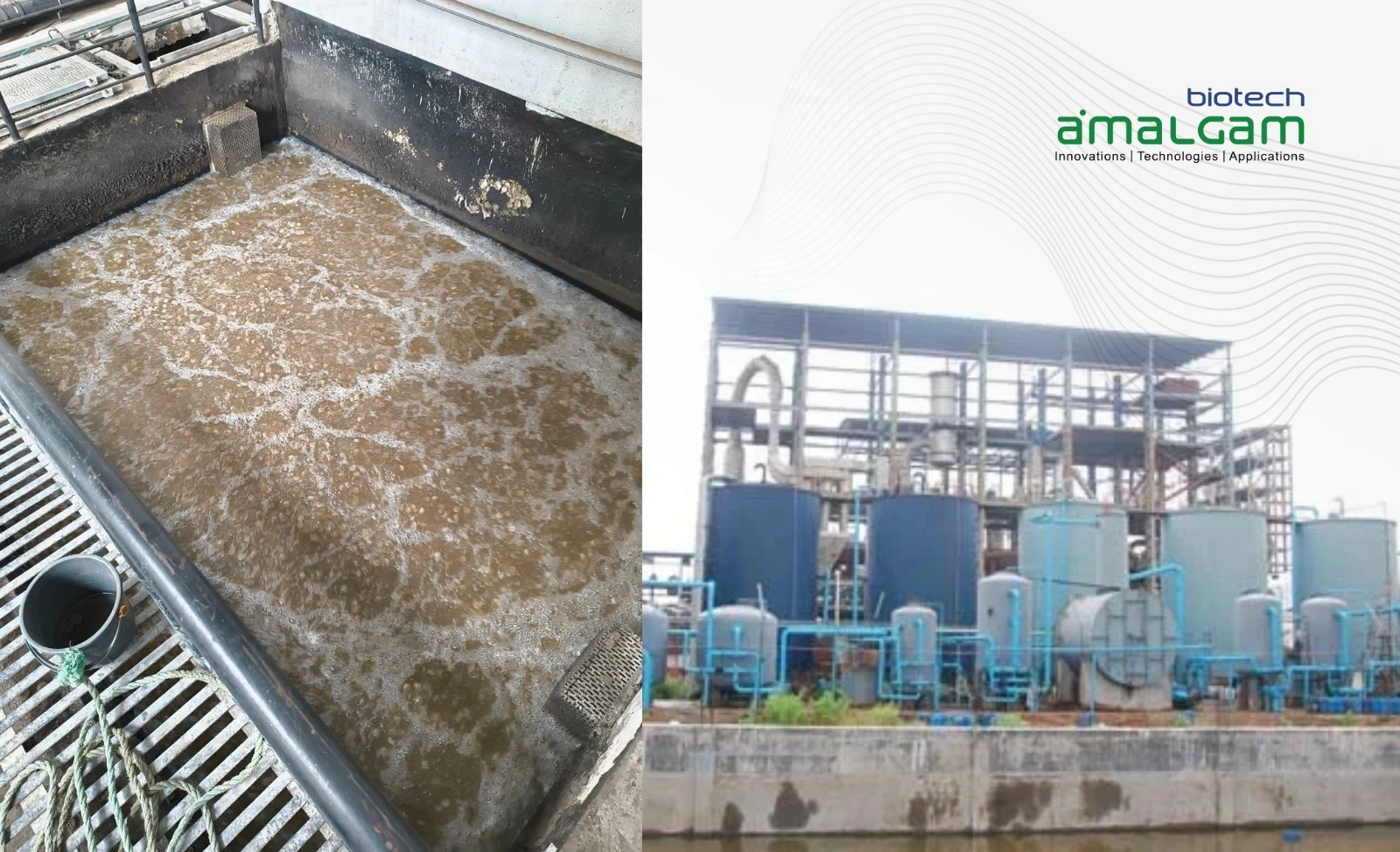
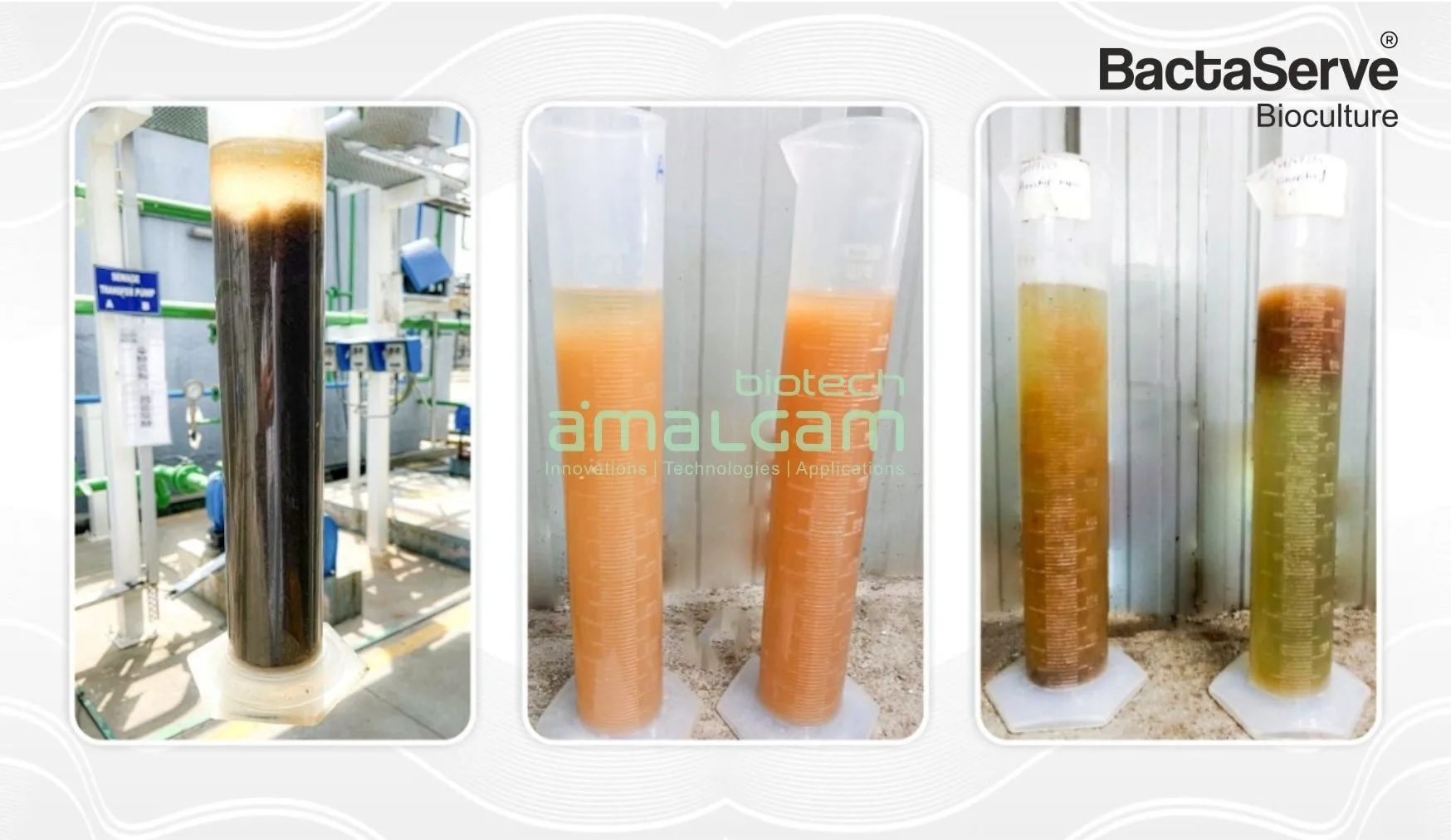
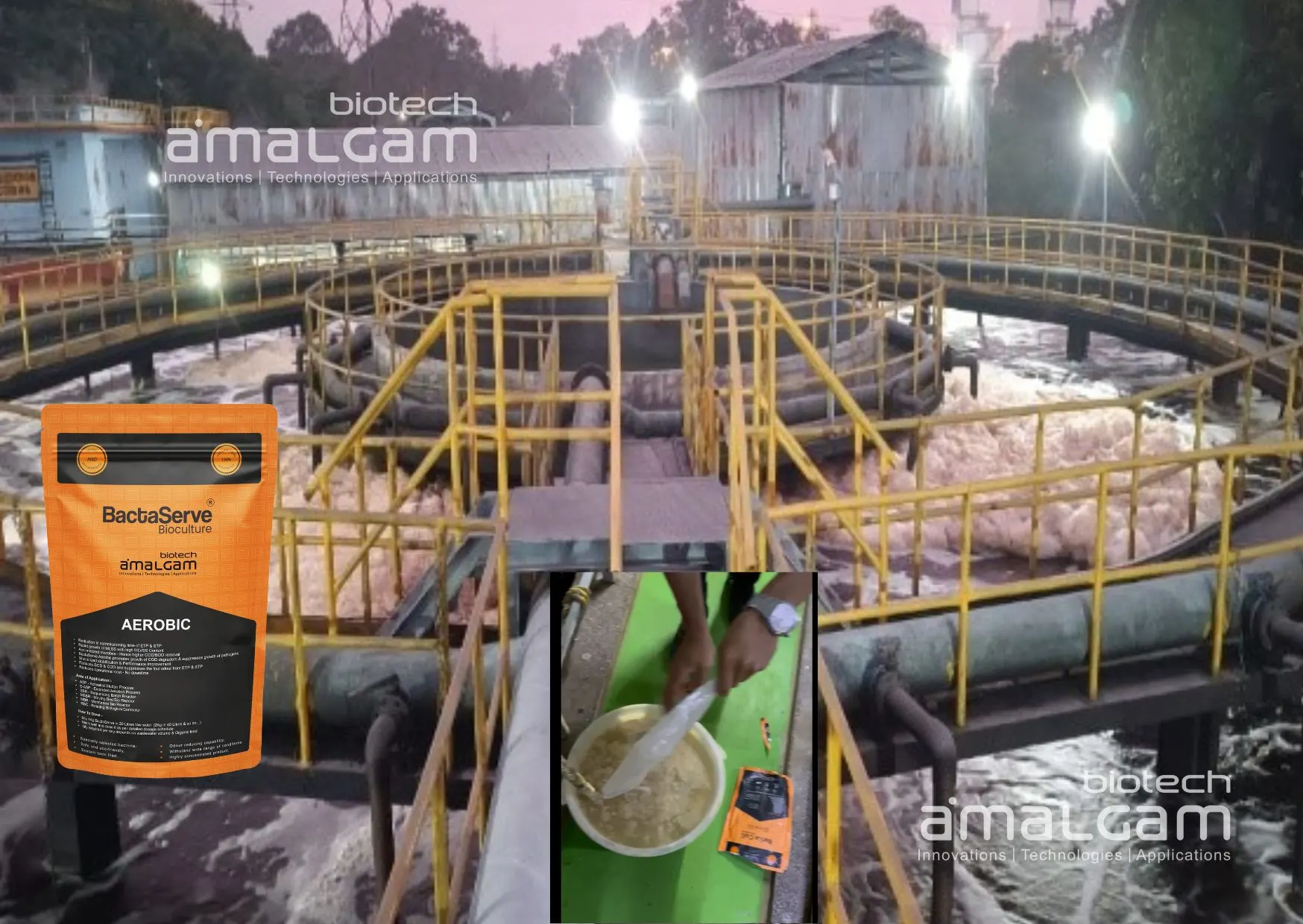
Water contamination is a pressing global issue that requires efficient and sustainable treatment technologies. Oxidation water treatment has emerged as a highly effective method for breaking down organic and inorganic pollutants in wastewater. This process plays a crucial role in industrial and municipal wastewater treatment, helping to remove harmful contaminants, improve water quality, and ensure compliance with environmental regulations.
One of the most advanced forms of oxidation water treatment is chemical oxidation in wastewater treatment, which utilizes oxidizing agents to eliminate pollutants at a molecular level. This method has been widely adopted across various industries, offering a reliable and eco-friendly approach to wastewater management.
Understanding Oxidation Water Treatment
Oxidation in water treatment refers to a process in which oxidizing agents interact with contaminants to break them down into harmless compounds. This method is particularly effective for treating industrial effluents, hazardous organic compounds, and even certain metals. The oxidation process can be categorized into two main types:
- Biological Oxidation: Utilizes microorganisms to break down organic pollutants in wastewater.
- Chemical Oxidation: Uses strong oxidizing chemicals to degrade pollutants and disinfect water.
Among these, chemical oxidation in wastewater treatment is the most effective for handling complex pollutants that biological methods may not fully degrade.
Chemical Oxidation in Wastewater Treatment: How It Works
Chemical oxidation in wastewater treatment involves the addition of strong oxidants to wastewater, which react with contaminants to form less harmful substances. The most commonly used oxidants include:
- Chlorine and Hypochlorite: Effective in disinfection and oxidation of organic matter.
- Ozone (O3): A powerful oxidant that rapidly breaks down pollutants without leaving harmful residues.
- Hydrogen Peroxide (H2O2): Often used in combination with other oxidants for enhanced treatment.
- Potassium Permanganate (KMnO4): Applied in water treatment for removing iron, manganese, and organic contaminants.
- Fenton’s Reagent (H2O2 + Fe2+): A strong oxidation process that generates hydroxyl radicals for the breakdown of persistent pollutants.
Benefits of Oxidation Water Treatment
- Efficient Removal of Contaminants
- Eliminates organic pollutants, heavy metals, and pathogens.
- Reduces chemical oxygen demand (COD) and biological oxygen demand (BOD), improving water quality.
- Disinfection and Pathogen Control
- Kills bacteria, viruses, and other microorganisms without harmful residuals.
- Prevents the spread of waterborne diseases.
- Enhanced Water Clarity and Aesthetics
- Removes color, odor, and turbidity from wastewater.
- Improves the overall aesthetic appeal of treated water.
- Compatibility with Other Treatment Methods
- Can be integrated with biological treatment, filtration, and advanced oxidation processes (AOPs).
- Works efficiently in combination with coagulants and flocculants.
Applications of Chemical Oxidation in Wastewater Treatment
Chemical oxidation in wastewater treatment is widely used in multiple industries, including:
- Municipal Wastewater Treatment Plants (WWTPs): Helps in treating sewage and ensuring safe discharge of effluents.
- Industrial Wastewater Treatment: Applied in sectors like pharmaceuticals, textiles, pulp and paper, and petrochemicals to remove hazardous contaminants.
- Drinking Water Purification: Used to disinfect and improve the quality of potable water.
- Landfill Leachate Treatment: Breaks down complex organic compounds in leachate before disposal.
- Agricultural Runoff Treatment: Mitigates the impact of fertilizers and pesticides in water sources.
Oxidation Technologies for Wastewater Treatment
Several advanced oxidation technologies are available to enhance oxidation water treatment efficiency. These include:
1. Ozone-Based Oxidation
Ozone is a highly effective oxidant used to break down organic contaminants and disinfect wastewater. It is particularly useful for treating pharmaceutical and textile effluents.
2. Fenton’s Oxidation Process
This method generates hydroxyl radicals, which have an exceptionally high oxidation potential. It is widely used in treating industrial wastewater containing refractory pollutants.
3. Electrochemical Oxidation
A process in which an electric current is applied to wastewater, generating oxidants such as hydroxyl radicals to degrade pollutants.
4. UV-Enhanced Oxidation
Combining ultraviolet (UV) radiation with oxidants such as hydrogen peroxide or ozone enhances the breakdown of organic contaminants.
5. Chlorine Dioxide (ClO2) Treatment
A strong oxidizing agent used for disinfection and removal of taste and odor compounds in water treatment.
Factors to Consider When Implementing Oxidation Water Treatment
To achieve the best results from chemical oxidation in wastewater treatment, several key factors must be considered:
- Type of Contaminants: The choice of oxidant depends on the nature of pollutants present in the wastewater.
- pH Levels: The efficiency of oxidation processes varies with pH; some oxidants work best in acidic or alkaline conditions.
- Reaction Time: The contact time between the oxidant and contaminants affects treatment efficiency.
- Oxidant Dosage: Proper dosage ensures complete pollutant breakdown without excess chemical use.
- Byproduct Formation: Some oxidation reactions produce secondary pollutants that may require further treatment.
Challenges and Future Developments
While oxidation water treatment is highly effective, certain challenges remain:
- High Operational Costs: Some oxidation methods require significant energy input, increasing treatment costs.
- Formation of Byproducts: Some oxidants produce undesirable byproducts that must be managed carefully.
- Handling of Strong Oxidants: Certain chemicals used in oxidation require special handling and storage precautions.
To address these challenges, ongoing research is focused on:
- Developing Cost-Effective Oxidants: Efforts are being made to create sustainable and economical oxidizing agents.
- Enhancing Treatment Efficiency: Advancements in catalyst-based oxidation and hybrid treatment methods improve pollutant removal.
- Integrating Smart Technologies: AI and IoT-based monitoring systems are being integrated to optimize oxidation processes.
Conclusion
Oxidation water treatment is an essential component of modern wastewater management, offering an effective solution for removing contaminants and ensuring clean water discharge. By utilizing chemical oxidation in wastewater treatment, industries and municipalities can enhance treatment efficiency, comply with environmental regulations, and contribute to sustainable water resource management. As new advancements continue to emerge, oxidation-based treatment will play an increasingly vital role in achieving water purity and environmental conservation.