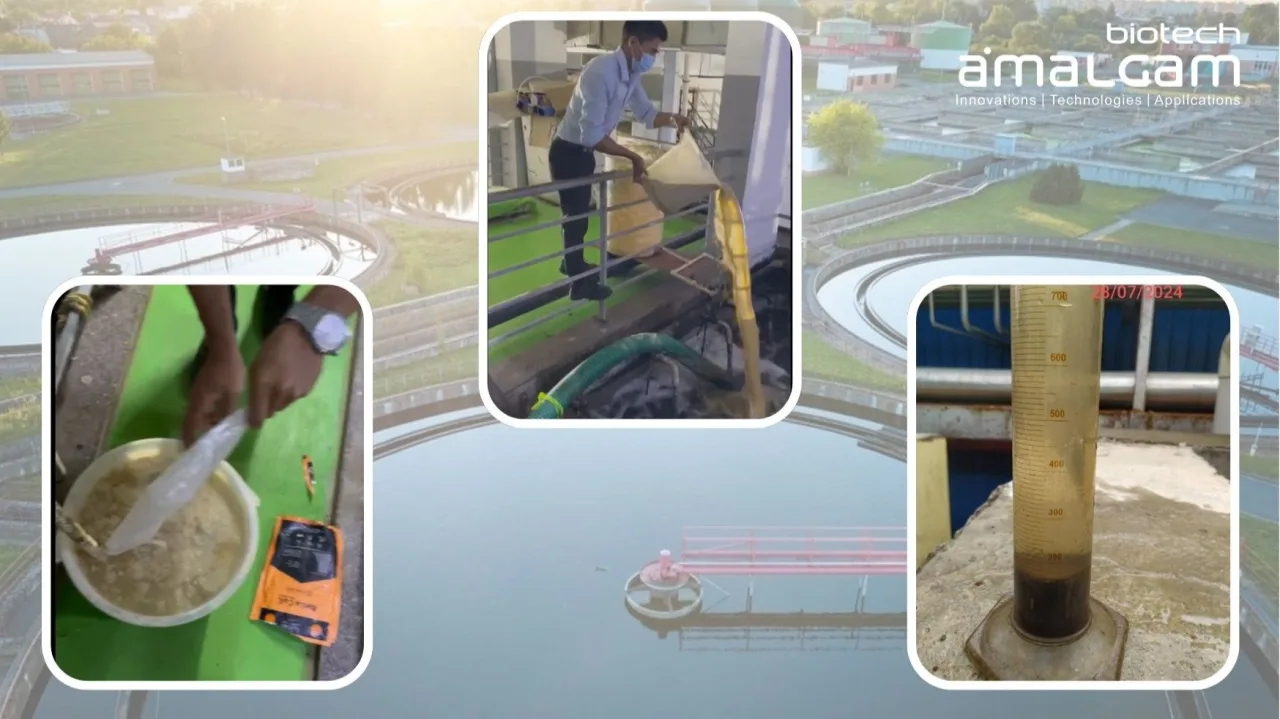
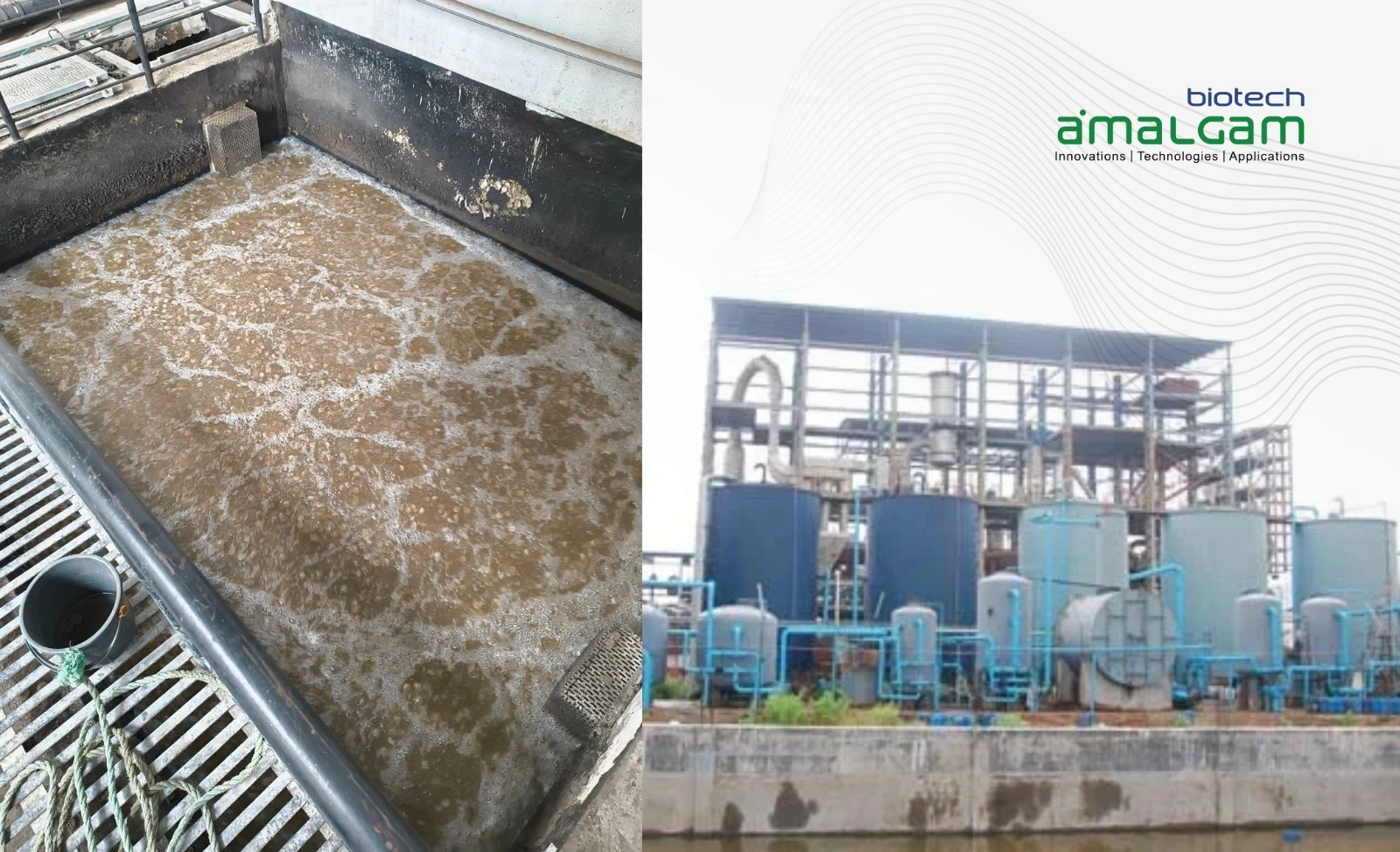
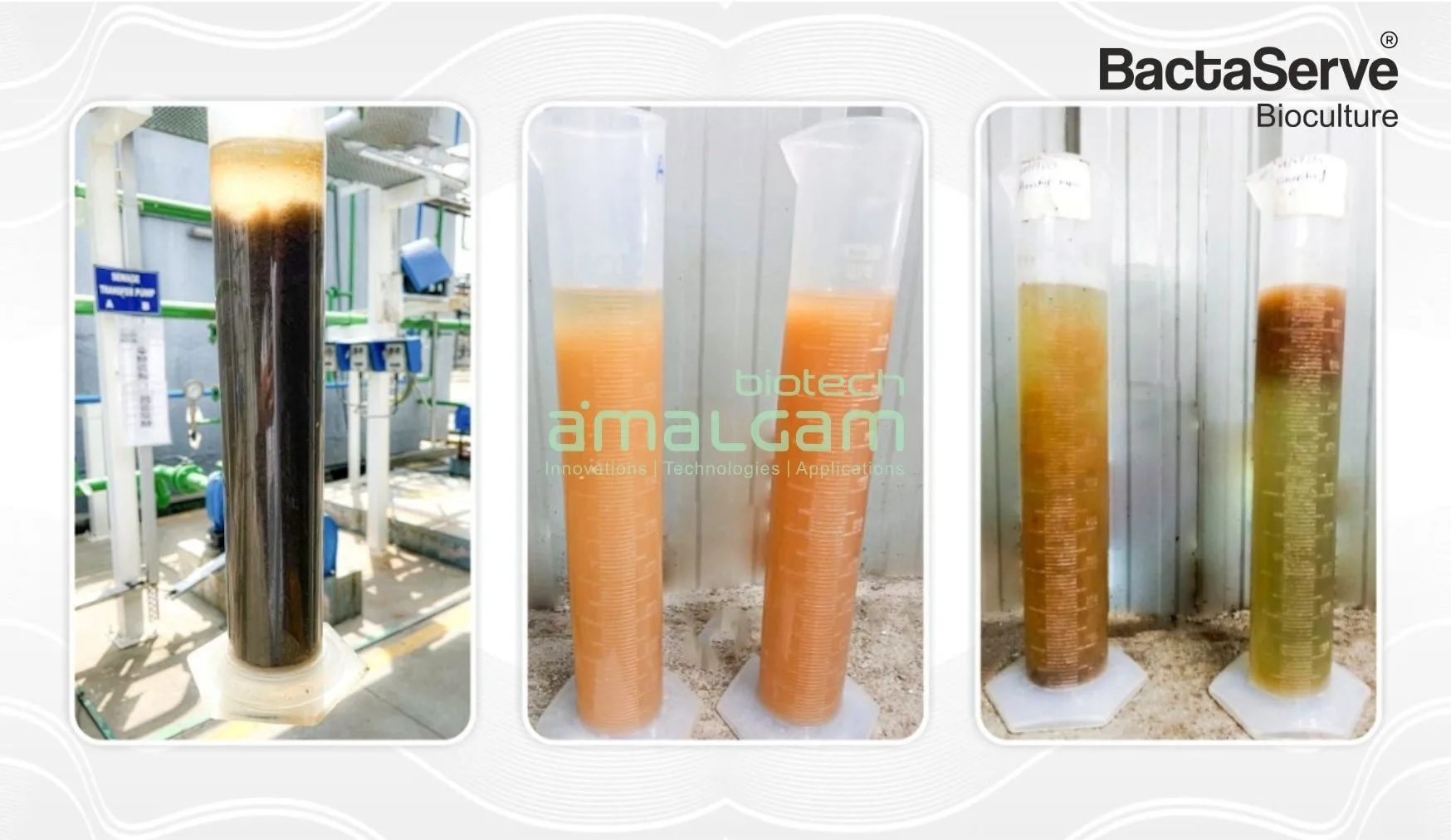
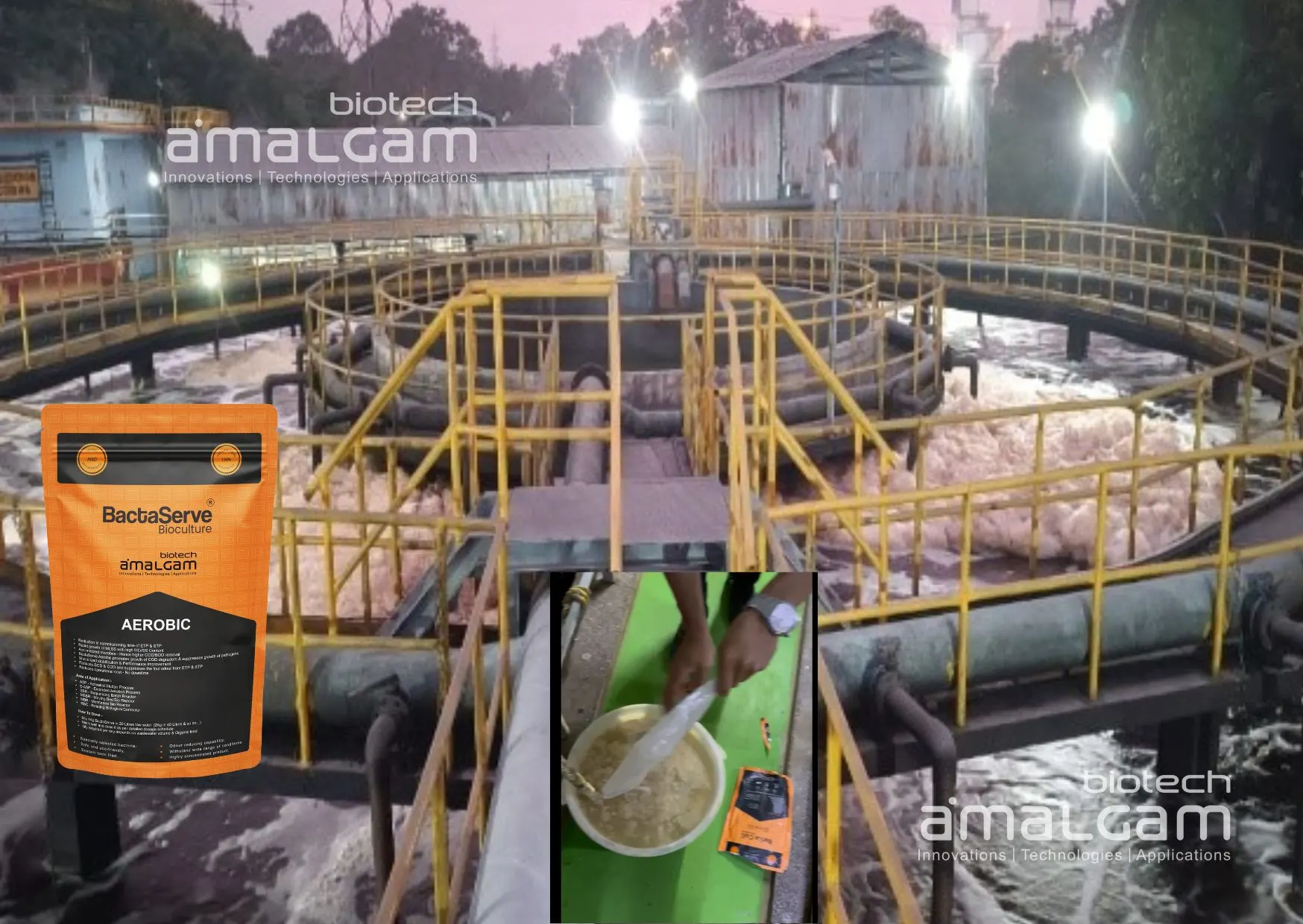
In today's world, environmental sustainability is paramount. Industries are constantly seeking ways to minimize their environmental impact while ensuring efficient operations. For Sewage Treatment Plants (STPs), stp bio culture emerges as a powerful tool to achieve both.
What is STP Bio Culture?
Stp bio culture refers to the introduction of specifically cultivated microbial consortia into the biological treatment processes within an STP.
These carefully selected microorganisms are designed to enhance the natural biological processes that break down organic matter and remove pollutants from wastewater. Unlike relying solely on the naturally occurring microbial populations within the STP, stp bio culture introduces a concentrated and diverse group of microorganisms specifically chosen for their ability to efficiently degrade a wider range of pollutants and improve overall treatment performance.
How Does STP Bio Culture Work?
Stp bio culture works by augmenting the existing microbial population within the STP. These introduced microorganisms possess unique metabolic capabilities, enabling them to:
Degrade Complex Pollutants: Stp bio culture can effectively degrade a wider range of organic pollutants, including those that are difficult to break down by the native microbial population. This includes complex compounds like hydrocarbons, phenols, and dyes often found in industrial wastewater. These specialized microorganisms possess enzymes that can break down these complex molecules, leading to more complete pollutant removal and improved effluent quality.
Accelerate Treatment Processes: By introducing highly active microorganisms, stp bio culture accelerates the rate of organic matter degradation and pollutant removal. This leads to shorter treatment times and improved overall treatment efficiency. For example, in activated sludge processes, stp bio culture can significantly enhance the rate of sludge floc formation and organic matter oxidation, resulting in faster treatment cycles and reduced treatment times.
Enhance Nutrient Removal: Stp bio culture can significantly enhance the removal of nutrients like nitrogen and phosphorus from the wastewater. Excessive levels of these nutrients can contribute to water pollution and environmental problems such as eutrophication. Many stp bio culture formulations include specialized microorganisms that can effectively remove nitrogen through processes like nitrification and denitrification, and phosphorus through mechanisms such as biological phosphorus removal.
Reduce Sludge Volume: By improving the efficiency of organic matter degradation, stp bio culture can significantly reduce the amount of sludge produced within the STP. This minimizes the need for costly sludge disposal and reduces the environmental impact associated with sludge management. Sludge disposal can be a significant operational cost for STPs. By reducing sludge volume, stp bio culture helps to minimize these costs and reduce the environmental burden associated with sludge disposal methods such as landfilling or incineration.
Benefits of Using STP Bio Culture
Implementing stp bio culture offers numerous advantages for STPs:
Improved Effluent Quality: By enhancing the treatment process, stp bio culture ensures that the treated effluent meets stringent environmental regulations and can be safely discharged or reused. This not only protects the environment but also opens up opportunities for water reuse, such as for irrigation or industrial processes, contributing to water conservation efforts.
Reduced Operational Costs: Increased treatment efficiency translates to lower energy consumption, reduced chemical usage, and minimized sludge disposal costs, resulting in significant cost savings for the plant. By reducing treatment times and improving overall plant performance, stp bio culture can lead to substantial cost savings for the plant operator.
Enhanced Sustainability: Stp bio culture promotes sustainable wastewater treatment practices by minimizing environmental impact and contributing to a greener future. By reducing sludge volume, minimizing chemical usage, and improving treatment efficiency, stp bio culture contributes to a more environmentally friendly and sustainable wastewater treatment process.
Improved Compliance: By ensuring that the treated effluent meets regulatory standards, stp bio culture helps industries maintain compliance with environmental regulations and avoid potential penalties. This not only protects the environment but also safeguards the industry's reputation and ensures long-term business viability.
Increased Treatment Plant Stability: Stp bio culture can help to stabilize the treatment process, making it less susceptible to fluctuations in wastewater quality and operating conditions. This improves the overall reliability and consistency of the treatment plant, ensuring consistent effluent quality and minimizing the risk of treatment failures.
Selecting the Right STP Bio Culture
The effectiveness of stp bio culture depends heavily on selecting the right microbial consortium for the specific wastewater characteristics of the plant. Factors such as the type of industry, the nature of the wastewater, and the desired treatment goals should be carefully considered.
Industry-Specific Solutions: Different industries generate wastewater with varying compositions and levels of pollution. Therefore, it is crucial to select a stp bio culture that is specifically formulated to address the unique challenges of a particular industry, such as the textile, food processing, or pharmaceutical industry. For example, a stp bio culture designed for the textile industry may be more effective at degrading dyes and other chemicals commonly found in textile wastewater.
Wastewater Characteristics: The characteristics of the wastewater, such as pH, temperature, and the presence of specific pollutants, will influence the selection of the most appropriate stp bio culture. Some stp bio culture formulations are more effective at operating in specific temperature ranges or pH levels, while others are specifically designed to degrade certain types of pollutants.
Treatment Goals: The specific treatment goals, such as achieving a certain level of pollutant removal or meeting specific regulatory requirements, should be considered when selecting a stp bio culture. For instance, if the goal is to achieve a very low level of nitrogen in the effluent, a stp bio culture that is specifically designed for enhanced nitrogen removal would be more suitable.
Customized Solutions: In some cases, customized stp bio culture solutions may be required to address unique treatment challenges or to optimize performance in specific operating conditions. These customized solutions can be tailored to the specific needs of a particular industry or STP, ensuring maximum effectiveness and addressing the unique challenges of the specific wastewater stream.
Implementation of STP Bio Culture
The successful implementation of stp bio culture requires careful planning and execution. Key steps include:
Assessment of Wastewater Characteristics: A thorough analysis of the wastewater characteristics, including its chemical composition, temperature, and pH, is essential to determine the appropriate type and dosage of stp bio culture. This analysis will help ensure that the selected stp bio culture is well-suited to the specific challenges of the wastewater and will provide the foundation for a successful implementation.
Selection and Sourcing of Bio Culture: Choose a reputable supplier that provides high-quality, well-characterized stp bio culture with a proven track record of success. It is crucial to select a supplier that can provide technical support and guidance on the proper application and maintenance of the stp bio culture.
Proper Application and Monitoring: Stp bio culture should be applied according to the supplier's recommendations and monitored regularly to ensure optimal performance. Regular monitoring involves analyzing key parameters such as pH, dissolved oxygen, and pollutant levels to ensure that the stp bio culture is effectively treating the wastewater and achieving the desired treatment goals.
Maintenance of Treatment Plant Conditions: Maintaining optimal operating conditions within the STP, such as proper aeration, mixing, and temperature control, is crucial for maximizing the effectiveness of the stp bio culture. These conditions can significantly impact the activity and efficiency of the microorganisms within the stp bio culture, ensuring that they can thrive and effectively perform their treatment functions.
Case Studies
Numerous case studies have demonstrated the successful application of stp bio culture across various industries, resulting in significant improvements in effluent quality, reduced operational costs, and enhanced environmental sustainability. These case studies provide valuable insights into the real-world benefits of implementing stp bio culture and can serve as a valuable resource for industries considering this approach.
Conclusion
Stp bio culture offers a powerful and sustainable solution for enhancing wastewater treatment processes. By harnessing the power of microbial diversity, stp bio culture can significantly improve treatment efficiency, reduce environmental impact, and contribute to a cleaner and more sustainable future. By embracing stp bio culture, industries can not only meet environmental regulations but also achieve significant cost savings and improve their overall environmental performance.